At the end of 2017, a new microalgae, Haematococcus pluvialis, and its extract astaxanthin were authorized for human consumption by the European Commission (1, 2).
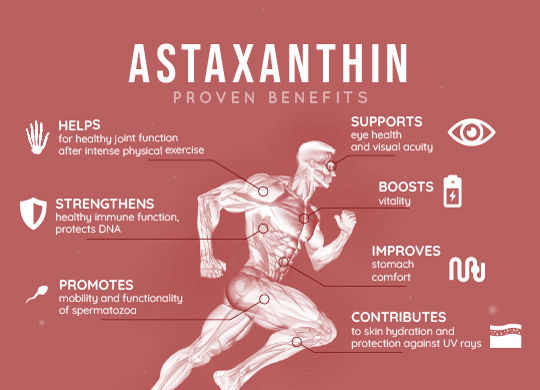
Astaxanthin, extracted from the microalgae Haematococcus pluvialis, has entered the list of novel foods or food supplements defined by the European Commission on novel foods, in accordance with regulation(novel food) (EU) 2015/2283 (3). These recommendations are for healthy adults only.
Pour bien vous accompagner
Discover our guides
Astaxanthin: definition, origin, explanation

They are synthesized by all plants as they play a major role in photosynthesis, the reaction that uses carbon dioxide and light to produce organic compounds and oxygen (4).
Salmon, lobster, shrimp and even flamingos have pretty orange colors because they eat algae containing carotenoids.
Astaxanthin is a bright red pigment. It is naturally produced by the microalgae Haematococcus pluvialis. The natural Astaxanthin dietary supplement is therefore an extract of this microalgae, but it can also be produced by chemical synthesis. It is this much cheaper synthetic product that is used to feed farmed salmon or trout to give their flesh an attractive orange color.
Astaxanthin has particularly interesting effects on our bodies, and scientists explain its health benefits by the fact that it is a powerful antioxidant ( 4).
Premium Natural Organic Astaxanthin

TRIAL OFFER: 2 x 30 capsules = 2 MONTHS
59.90 €
54.99 €
Astaxanthin dosage and benefits
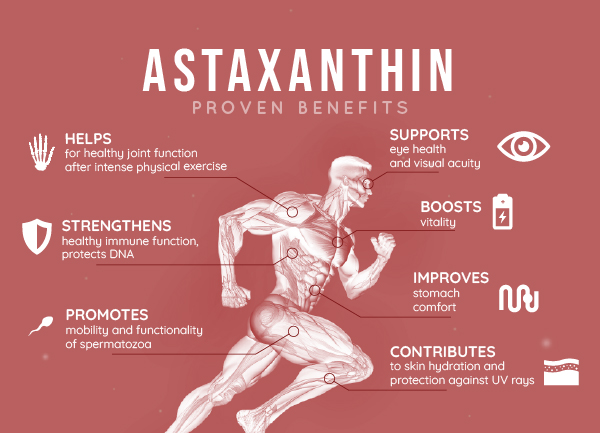
The European Commission’s text mentions an authorization for a consumption recommendation of up to 80 mg of Haematococcus pluvialis oleoresin, i.e. 8 mg astaxanthin per day (2).
Clinical studies carried out in Japan show that a daily intake of 4 mg astaxanthin provides significant protection of the skin against the effects of UV rays, and that a daily intake of 6 mg shows an skin improvement on elasticity, wrinkles, dryness, age spots and eyes (5).
Top athletes use minimum doses of 16 mg a day(*).
Among the scientific publications reporting on astaxanthin’s efficacy, some studies have been carried out using high doses: from 40 mg to 100 mg per day. A dose of 40 mg per day was shown to improve gastric reflux syndrome as early as 4 weeks. Gastric reflux is well reduced in people infected with Helicobacter piloris (6, 7). (*)
The maximum amount of astaxanthin present in the blood appears between 8 and 10 h after taking 40 mg (8).
(*) According to European Parliament Directive 2002/46/EC, the maximum authorized doses of astaxanthin-rich oleoresin extracted from Haematococcus pluvialis algae for the general population are currently between 40 and 80 mg oleoresin per day, equivalent to less than 8.0 mg astaxanthin per day. The new Commission Implementing Regulation (EU) 2021/1377 of August 19, 2021 requests that it be clarified that this dietary supplement should not be used for children under the age of 14.
When should astaxanthin be taken during the day?
Side effects of astaxanthin?
What are the contraindications to taking astaxanthin?
No contraindications to astaxanthin have been identified to date. However, as a precautionary measure, astaxanthin is not recommended for pregnant or breast-feeding women, or for children under 14.
Can astaxanthin be taken in combination?
For anti-inflammatory (pain-relieving) effects, the combination of chlorella and astaxanthin may make sense.
Remember: chlorella should be taken in the morning on an empty stomach, while spirulina should be taken in the evening before a meal. Astaxanthin is best taken during or after a meal, as it is better assimilated in the presence of lipids (11, 12, 13, 14).
Where can I buy astaxanthin?
Natural Organic Astaxanthin

Trial offer ( 2 x 30 ) | 8 mg – Premium Astaxanthin

